Bone Marrow Transplant
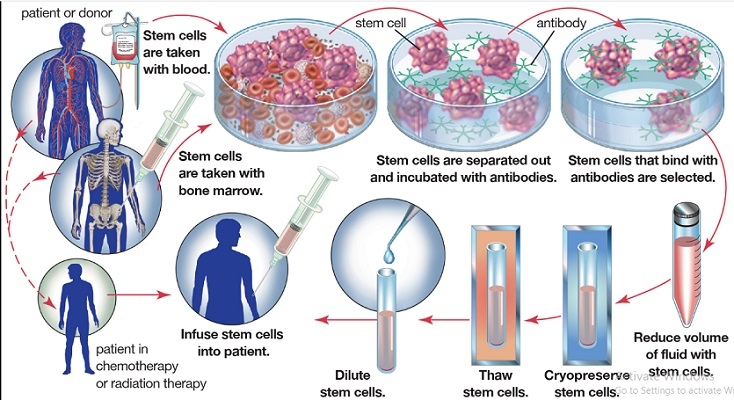
Bone Marrow transplant is a special procedure used to treat a variety of disorders.
It is of two types:
- Autologous stem cell transplant: When the patients stem cells are used for himself. Here the patient’s stem cells are harvested and stored. Chemotherapy is given and then stem cells are reinfused.
- Allogenic Stem cell transplant: When another person’s stem cells are used. The person giving his stem cells is called a donor.
Donors can be
Matched related transplant: These are family members having a 6/6 or 10/10 HLA match with the patient
Matched unrelated transplant: These donors are unrelated people who share a 10/10 HLA match with the recipient
Haploidentical Transplant: These donors are family members without a complete match having more than 5/10 match with the patient.
Steps of Transplant:
- Hickman insertion: A special line is inserted to facilitate the process of giving medications and infusing blood and stem cells.
- Conditioning regimen: Chemotherapy is given via injections before the transplant to the patient. The purpose is to destroy the diseased bone marrow.
- Stem Cell Transfusion: The stem cells collected from the donor are transfused via the Hickman line
- GvHD prophylaxis: These are medicines given to prevent the reactions of transplant
Engraftment:
This is when the patient WBC and platelet starts increasing. This is the earliest sign of recovery and a sign of success of transplant.
Source of stem cells:
- Peripheral blood stem cells: Here given an injection for 5 days to mobilize the stem cells in the blood. The donor is then connected to apheresis machine and stem cells are collected from the donor
- Bone Marrow stem cells: Here the donors is sedated and stem cells are connected directly from the bone marrow
- Cord blood stem cells: Here the stored cord blood cells collected at the time of birth of baby are used for the transplant.



